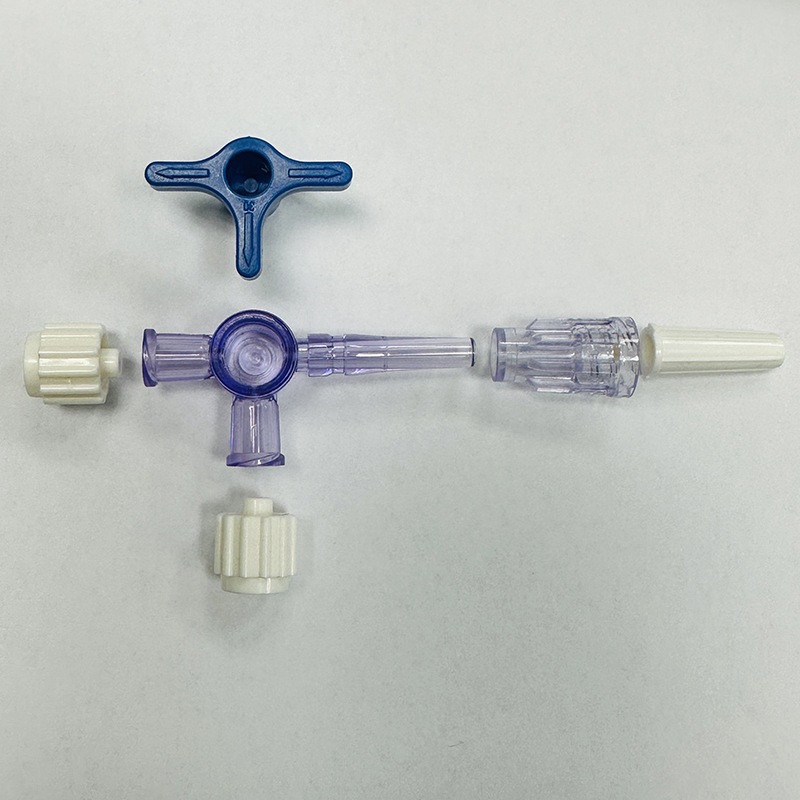
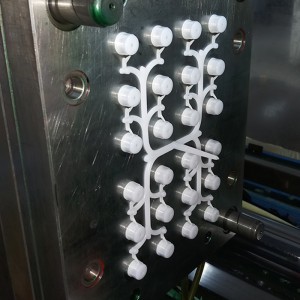
A stopcock mold is a tool used in the manufacturing process to produce stopcocks, which are valves used to control the flow of liquids or gases in various applications, such as medical devices or laboratory equipment. Here are three ways a stopcock mold works:Mold Design and Cavity Creation: The stopcock mold is designed to create the desired shape and functionality of the stopcock. It consists of two or more halves, usually made of steel, that come together to form one or multiple cavities where the molten material is injected. The mold design includes the necessary features, such as inlet and outlet ports, sealing surfaces, and control mechanisms, to ensure proper operation of the stopcock.Molten Material Injection: Once the mold is set up and securely closed, the molten material, typically a thermoplastic or elastomeric material, is injected into the cavities under high pressure. The injection is performed using specialized machinery, such as an injection molding machine, that forces the material through channels and into the mold cavities. The material fills the cavities, taking the shape of the stopcock design.Cooling and Ejection: After the molten material is injected into the mold, it is left to cool and solidify. Cooling can be facilitated by circulating a coolant through the mold or using cooling plates. Once the material has solidified, the mold is opened, and the finished stopcock is ejected from the cavities. Ejection can be achieved through various mechanisms, such as ejector pins or air pressure. Quality control measures, including inspections for defects and dimensional accuracy, may be performed at this stage to ensure the stopcock meets the required specifications.Overall, a well-designed and precisely manufactured stopcock mold is crucial for producing high-quality stopcocks that function reliably. The mold allows for the efficient and consistent production of stopcocks, which are widely used in various industries for fluid control applications.