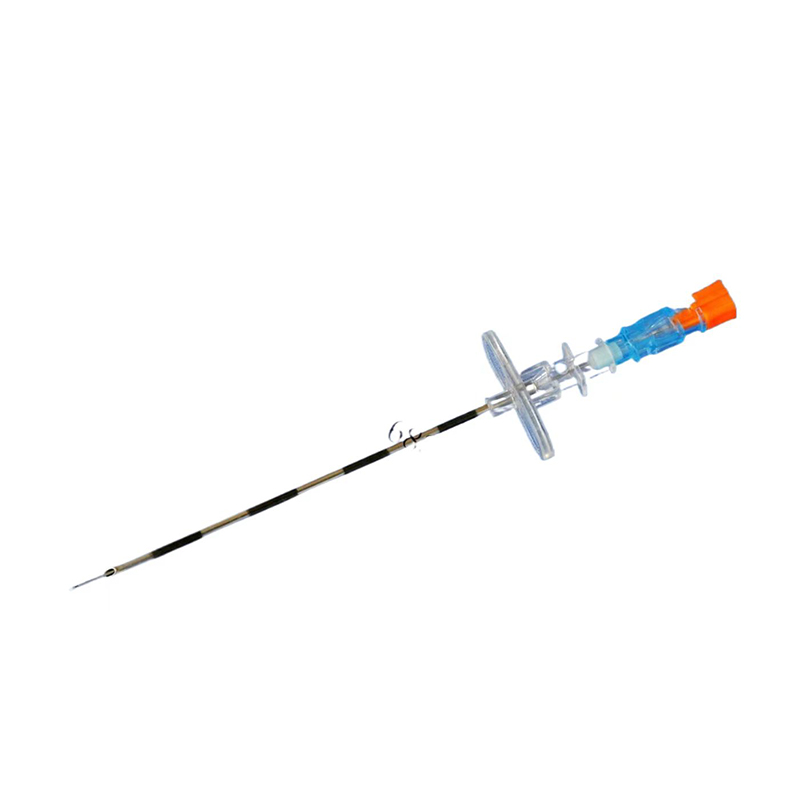
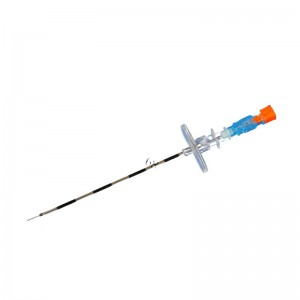
Spinal Needle And Epidural Needle
1. Preparation:
- Ensure that the packaging of the disposable lumbar puncture needle is intact and sterile.
- Clean and disinfect the patient's lower back area where the lumbar puncture will be performed.
2. Positioning:
- Position the patient in a suitable position, usually lying on their side with their knees drawn up towards their chest.
- Identify the appropriate intervertebral space for the lumbar puncture, usually between the L3-L4 or L4-L5 vertebrae.
3. Anesthesia:
- Administer local anesthesia to the patient's lower back area using a syringe and needle.
- Insert the needle into the subcutaneous tissue and slowly inject the anesthetic solution to numb the area.
4. Lumbar Puncture:
- Once the anesthesia takes effect, hold the disposable lumbar puncture needle with a firm grip.
- Insert the needle into the identified intervertebral space, aiming towards the midline.
- Advance the needle slowly and steadily until it reaches the desired depth, usually around 3-4 cm.
- Observe for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and collect the required amount of CSF for analysis.
- After collecting the CSF, slowly withdraw the needle and apply pressure to the puncture site to prevent bleeding.
4. Spinal Needle:
- Once the anesthesia takes effect, hold the disposable spinal needle with a firm grip.
- Insert the needle into the desired intervertebral space, aiming towards the midline.
- Advance the needle slowly and steadily until it reaches the desired depth, usually around 3-4 cm.
- Observe for the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and collect the required amount of CSF for analysis.
- After collecting the CSF, slowly withdraw the needle and apply pressure to the puncture site to prevent bleeding.
Purposes:
Disposable epidural needles and spinal needles are used for diagnostic and therapeutic procedures involving the collection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). These procedures are commonly performed to diagnose conditions such as meningitis, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and certain neurological disorders. The collected CSF can be analyzed for various parameters, including cell count, protein levels, glucose levels, and the presence of infectious agents.
Note: It is crucial to follow proper aseptic techniques and dispose of the used needles in designated sharps containers according to medical waste disposal guidelines.